If chloroplasts and mitochondria could speak, they would have a fascinating conversation about their essential roles in cellular life. This engaging exploration delves into their functions, interactions, and profound impact on the health of the cell.
As the powerhouses of the cell, chloroplasts and mitochondria play pivotal roles in photosynthesis and energy production. Their symbiotic relationship with the eukaryotic cell is a testament to the intricate harmony of life’s processes.
Chloroplast and Mitochondria: The Powerhouses of the Cell

Chloroplasts and mitochondria are two essential organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert glucose into energy.
Structure of Chloroplasts, If chloroplasts and mitochondria could speak
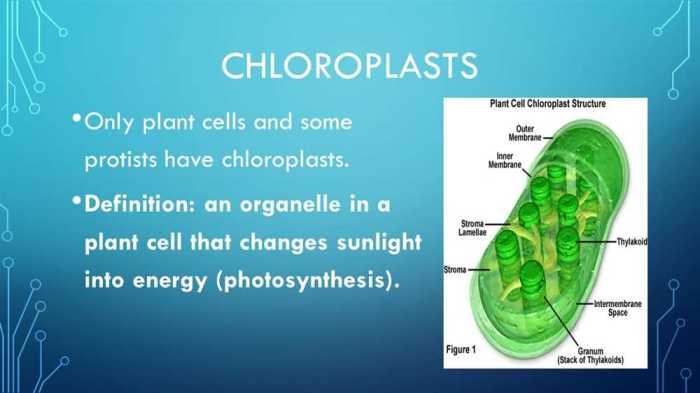
Chloroplasts are typically disk-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is folded into thylakoids, which are flattened sacs that contain chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs sunlight and uses it to power the reactions of photosynthesis.
Structure of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is folded into cristae, which are shelf-like structures that increase the surface area of the membrane. The cristae are where the enzymes involved in cellular respiration are located.
If Chloroplasts and Mitochondria Could Speak: A Conversation
Chloroplast: “Greetings, Mitochondrion. I am the Chloroplast, and I am responsible for providing energy to the cell through photosynthesis.”Mitochondrion: “And I am the Mitochondrion, responsible for converting glucose into energy through cellular respiration. Together, we are the powerhouses of the cell.”Chloroplast:
“Indeed. Our functions are complementary. I use sunlight to create glucose, which you then use to produce ATP.”Mitochondrion: “Yes, and in return, I provide you with the carbon dioxide you need for photosynthesis. It’s a beautiful symbiotic relationship.”
The Evolution of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by a larger cell. Over time, these bacteria lost their ability to live independently and became dependent on the host cell for survival.
Evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory
- Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own DNA, which is different from the DNA in the nucleus of the cell.
- Chloroplasts and mitochondria have ribosomes, which are structures that are used to make proteins.
- Chloroplasts and mitochondria can divide independently of the cell.
The Role of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria in Plant and Animal Cells
Chloroplasts are found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. This is because plants need to be able to photosynthesize, while animals do not. Mitochondria, on the other hand, are found in both plant and animal cells. This is because all cells need to be able to produce energy.
Functions of Chloroplasts in Plant Cells
Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts convert sunlight into energy, which is used to produce glucose.
Storage
Chloroplasts store starch, which is a complex carbohydrate that is used as an energy reserve.
Functions of Mitochondria in Plant and Animal Cells
Cellular respiration
Mitochondria convert glucose into energy, which is used to power the cell’s activities.
Heat production
Mitochondria produce heat as a byproduct of cellular respiration.
Chloroplasts and Mitochondria in Health and Disease
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are essential for human health. Malfunctions in these organelles can lead to a variety of diseases.
Chloroplast-Related Diseases
Chlorosis
A condition in which leaves turn yellow due to a lack of chlorophyll.
Albinism
A condition in which the body lacks melanin, which is a pigment that is produced by chloroplasts.
Mitochondria-Related Diseases
Mitochondrial myopathy
A condition that affects the muscles due to a malfunction in mitochondria.
Mitochondrial encephalopathy
A condition that affects the brain due to a malfunction in mitochondria.
The Future of Chloroplast and Mitochondria Research

Research on chloroplasts and mitochondria is ongoing, and there are many exciting new discoveries being made. One area of research is focused on developing new ways to use chloroplasts and mitochondria to produce renewable energy. Another area of research is focused on developing new treatments for diseases that are caused by malfunctions in these organelles.
Helpful Answers
What are the primary functions of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
How do mitochondria contribute to cellular energy production?
Mitochondria generate ATP through cellular respiration, providing the energy required for various cellular processes.
What is the significance of the endosymbiotic theory in understanding chloroplasts and mitochondria?
The endosymbiotic theory proposes that chloroplasts and mitochondria originated as independent prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by a larger cell, leading to their incorporation as organelles.