Embarking on an exploration of protons, neutrons, and electrons, this comprehensive guide unravels the fundamental building blocks of matter. Protons neutrons and electrons worksheet answers provide a roadmap for understanding the composition and behavior of atoms, paving the way for a deeper comprehension of the physical world.
Delving into the realm of subatomic particles, we will uncover the unique characteristics, properties, and interactions of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Through detailed explanations and illustrative examples, this discourse will illuminate the significance of these fundamental components in shaping the structure and reactivity of matter.
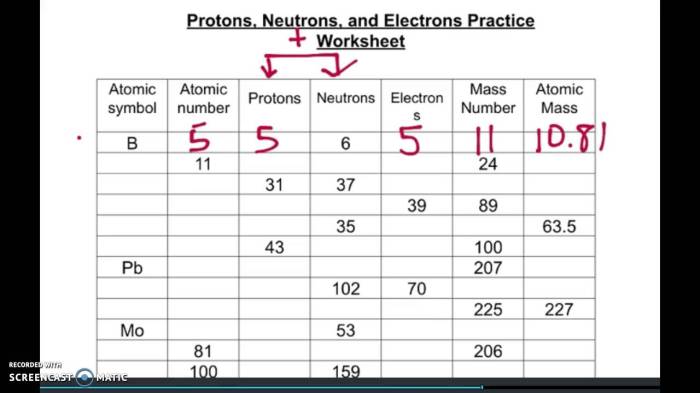
Protons: Protons Neutrons And Electrons Worksheet Answers
Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They contribute to an element’s atomic number and determine its chemical properties. Protons are made up of three quarks: two up quarks and one down quark.
Properties of Protons
- Charge: +1 elementary charge
- Mass: 1 atomic mass unit (amu)
- Location: Nucleus of the atom
- Stability: Stable within the nucleus
Examples of Elements Containing Protons
- Hydrogen: 1 proton
- Helium: 2 protons
- Oxygen: 8 protons
Neutrons
Neutrons are neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom. They contribute to an element’s atomic mass but not its atomic number. Neutrons are made up of three quarks: one up quark and two down quarks.
Properties of Neutrons
- Charge: 0 elementary charge
- Mass: 1 atomic mass unit (amu)
- Location: Nucleus of the atom
- Stability: Stable within the nucleus
Examples of Elements Containing Neutrons
- Hydrogen: 0 neutrons
- Helium: 2 neutrons
- Oxygen: 8 neutrons
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They contribute to an element’s chemical properties and determine its electrical conductivity. Electrons are fundamental to chemical reactions and electricity.
Properties of Electrons
- Charge: -1 elementary charge
- Mass: Negligible (1/1836 amu)
- Location: Electron cloud surrounding the nucleus
- Stability: Stable in electron shells
Examples of Elements Containing Electrons, Protons neutrons and electrons worksheet answers
- Hydrogen: 1 electron
- Helium: 2 electrons
- Oxygen: 8 electrons
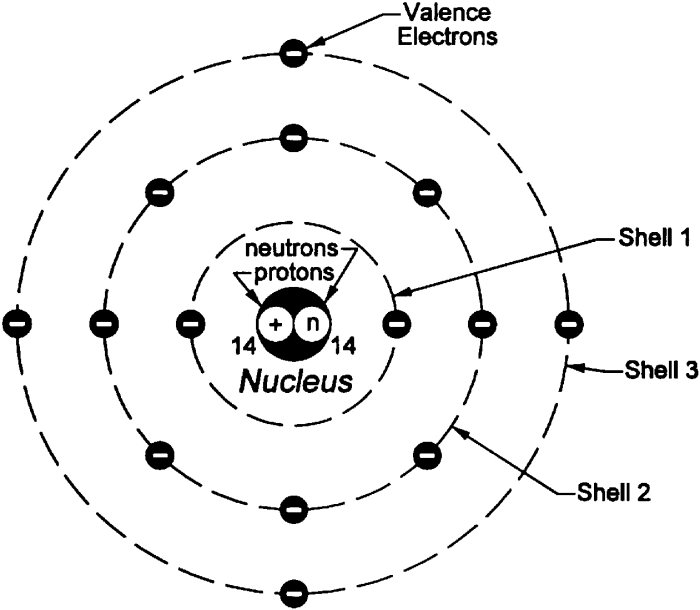
Atomic Structure
An atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
Arrangement of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Protons and neutrons are densely packed in the nucleus.
- Electrons occupy electron shells at varying distances from the nucleus.
- The number of protons determines the atomic number and the element’s identity.
- The number of neutrons affects the isotope of the element.
- The number of electrons determines the element’s chemical reactivity.
Diagram of Atomic Structure:
[Diagram of an atom with nucleus, protons, neutrons, and electrons labeled]
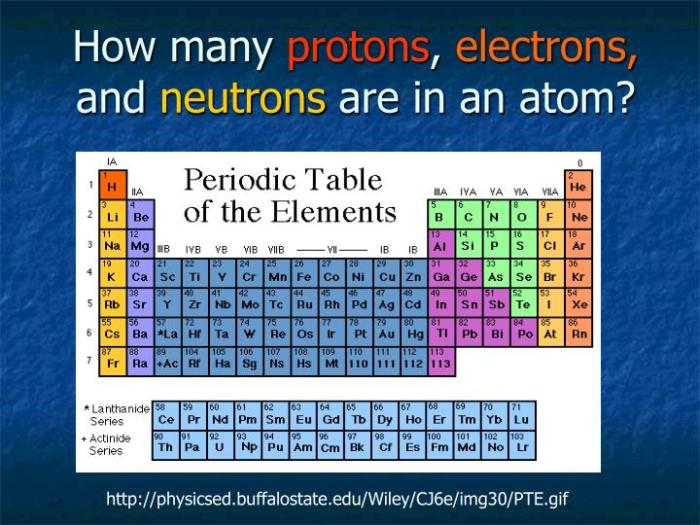
Periodic Table
The periodic table is an organized arrangement of elements based on their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
Contribution of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons to Periodic Table Position
- Atomic number (number of protons) determines an element’s position in a group (vertical column).
- Electron configuration (number and arrangement of electrons) determines an element’s position in a period (horizontal row).
- Neutrons affect the mass of an element and contribute to its isotopes.
Table of Elements with Proton, Neutron, and Electron Counts:
[Table showing elements with their corresponding proton, neutron, and electron counts]
Essential FAQs
What are the key differences between protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons carry a negative charge. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
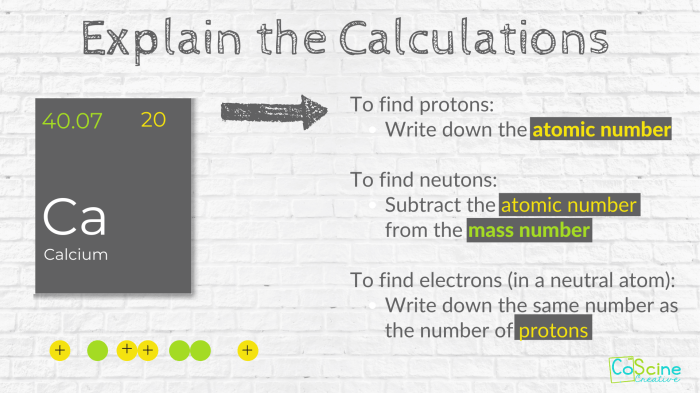
How do protons, neutrons, and electrons contribute to the atomic number and mass of an element?
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, while the mass number is determined by the combined number of protons and neutrons.
What is the significance of the periodic table in understanding the properties of elements?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and electron configuration, providing valuable insights into their chemical and physical properties.