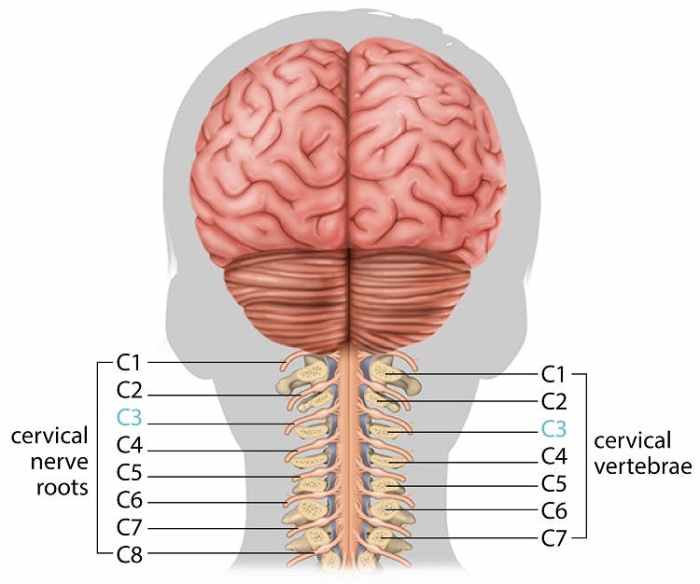
Injury to cervical vertebrae c3 c4 is particularly problematic because – Injury to cervical vertebrae C3-C4 is particularly problematic because of its critical role in supporting the head and neck. These vertebrae have unique structural features that make them vulnerable to injury, which can lead to serious neurological consequences. Understanding the mechanisms, symptoms, and treatment options for C3-C4 injuries is essential for optimal patient outcomes.
The anatomical significance of C3-C4 vertebrae, the mechanisms of injury, and the neurological consequences of these injuries will be explored in detail. The clinical presentation and diagnosis of C3-C4 injuries will also be discussed, along with the various treatment options available.
Finally, the prognosis and recovery from these injuries will be examined.
Anatomical Significance of Cervical Vertebrae C3-C4: Injury To Cervical Vertebrae C3 C4 Is Particularly Problematic Because
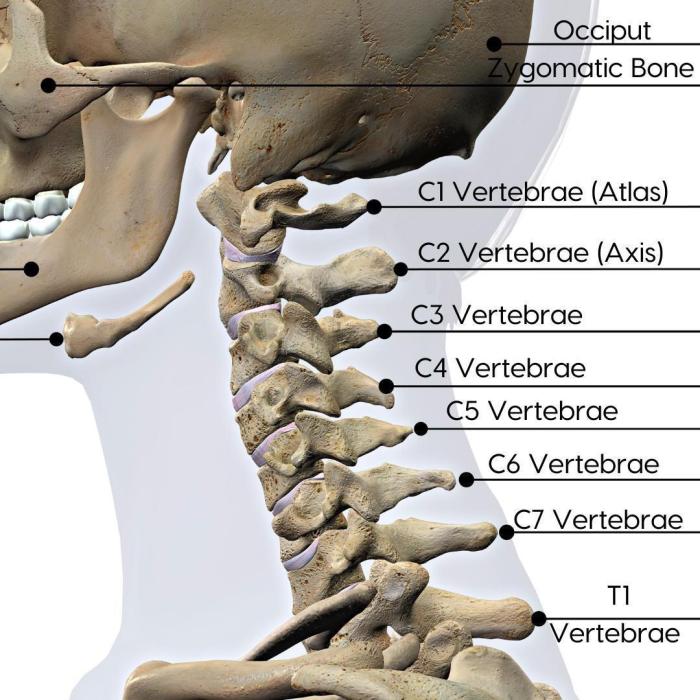
Cervical vertebrae C3 and C4 play a critical role in supporting the head and neck. These vertebrae form the junction between the skull and the rest of the cervical spine, providing stability and allowing for a wide range of head and neck movements.
C3 and C4 have unique structural features that contribute to their important role. They have large, flat articular surfaces that allow for smooth and gliding movements between the vertebrae. Additionally, they have strong ligaments and muscles that help to maintain the stability of the neck.
Mechanisms of Injury to Cervical Vertebrae C3-C4
Injuries to cervical vertebrae C3 and C4 can occur due to various mechanisms, including trauma and sports-related accidents. Trauma, such as a fall or a motor vehicle accident, can cause direct impact to the neck, leading to fractures or dislocations of C3 and C4.
Sports-related injuries, particularly in contact sports like football and rugby, can also result in C3-C4 injuries. These injuries often occur during tackles or collisions, where the head and neck are subjected to sudden and forceful movements.
Neurological Consequences of C3-C4 Injuries
Injuries to cervical vertebrae C3 and C4 can have significant neurological consequences. The spinal cord, which runs through the center of the vertebrae, can be damaged or compressed, leading to a range of neurological deficits.
These deficits can include weakness or paralysis in the arms and hands, loss of sensation in the upper limbs, and difficulty with balance and coordination. The severity of the neurological consequences depends on the extent and location of the injury.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of C3-C4 Injuries
The signs and symptoms of a C3-C4 injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Headache
- Weakness or paralysis in the arms and hands
- Loss of sensation in the upper limbs
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
To diagnose a C3-C4 injury, a thorough physical examination and imaging tests are necessary. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can help visualize the vertebrae and identify any fractures, dislocations, or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for C3-C4 Injuries, Injury to cervical vertebrae c3 c4 is particularly problematic because
The treatment options for C3-C4 injuries depend on the severity and type of injury. In some cases, conservative treatment, such as immobilization and pain medication, may be sufficient.
However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to stabilize the vertebrae, repair damaged ligaments, or decompress the spinal cord. Rehabilitation is also an important part of the treatment process, helping to restore range of motion, strength, and function to the neck and upper limbs.
Prognosis and Recovery from C3-C4 Injuries
The prognosis for C3-C4 injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury and the promptness of treatment. With early intervention and appropriate treatment, many patients can make a full or near-full recovery.
However, in some cases, severe injuries can result in permanent neurological deficits. Factors that influence the prognosis include the extent of spinal cord damage, the presence of associated injuries, and the patient’s overall health.
FAQ Overview
What are the common causes of C3-C4 injuries?
Common causes include trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports injuries.
What are the potential neurological deficits associated with C3-C4 injuries?
These injuries can affect motor function in the arms and hands, as well as sensory function in the neck and upper extremities.
How are C3-C4 injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, neurological testing, and imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs.
What are the treatment options for C3-C4 injuries?
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury and may include immobilization, surgery, and rehabilitation.